Flat Bar Rails
Flat bar rails and square bar rails are two common types of solid steel bars. Flat bars have a rectangular cross-section, while square bars have a square cross-section—hence the names. Their specifications are typically expressed in terms of width × thickness. For example, a 40×30mm flat bar means it is 40 mm wide and 30 mm thick. These steel bars have a wide range of uses: they can be directly used as crane rails or serve as raw materials for further processing. Common materials include Q235, Q355, and #45 steel.
Flat Bar Rail Key Features
Simple Cross-Section
Unlike standard rail profiles, flat bar rails have a rectangular cross-section, while square bars are square-shaped. This geometry allows for easy installation and maintenance, especially in flexible track layouts.
Weldable Connection
Flat and square bar rails do not require fishplates for joining. Instead, they can be directly welded using standard welding rods, offering a more seamless and efficient installation process.
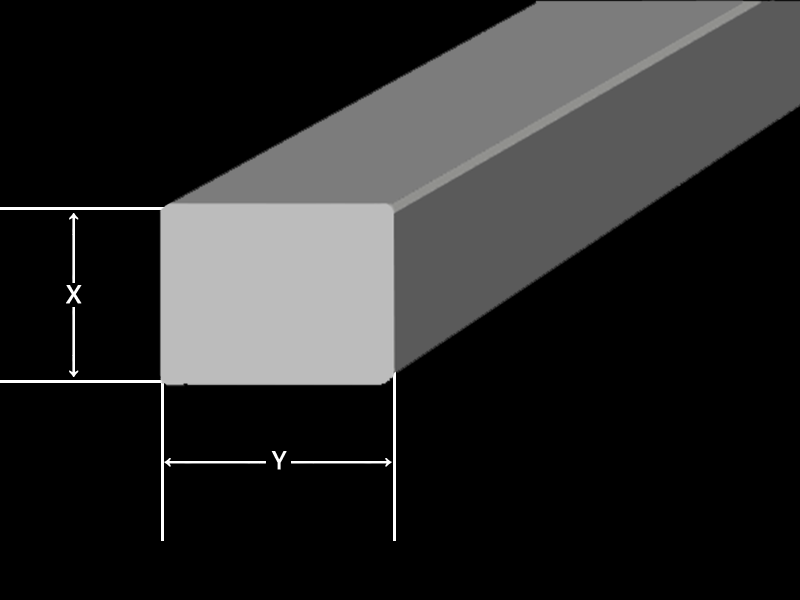
Flat Bar Rail Type
| Size | Height (mm) | Width (mm) | Weight (kg/m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | ||
| 40x30mm | 30 | 40 | 9.42 |
| 50x30mm | 30 | 50 | 11.775 |
| 60x40mm | 40 | 60 | 18.84 |
| 65x40mm | 40 | 65 | 20.41 |
| 70x40mm | 40 | 70 | 21.98 |
| 75x40mm | 40 | 75 | 23.55 |
| 80x60mm | 60 | 80 | 37.68 |
| 90x40mm | 40 | 90 | 28.26 |
| 100x60mm | 60 | 100 | 47.1 |
Square Bar Rail Type
| Size | Height (mm) | Width (mm) | Weight (kg/m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | ||
| 30x30mm | 30 | 30 | 7.065 |
| 40x40mm | 40 | 40 | 12.56 |
| 50x50mm | 50 | 50 | 19.625 |
| 60x60mm | 60 | 60 | 28.26 |
| 70x70mm | 70 | 70 | 38.465 |
| 80x80mm | 80 | 80 | 50.24 |
| 90x90mm | 90 | 90 | 63.585 |
| 100x100mm | 100 | 100 | 78.5 |
| 110x110mm | 110 | 110 | 94.985 |



Flat Bar Rails Applications
Crane Tracks: Available in various sizes tailored to match light-duty crane wheels.
Precision Parts: Cold-drawn flat bars serve as high-quality raw materials for manufacturing precision components.
Construction: Commonly used in structural components such as support columns and steel beams.
Machinery: Suitable for shafts, die blanks, and mechanical parts.
Decorative Engineering: Square bars are often used for framing doors and windows, stair railings, and other decorative metalwork.
Manufacturing Processes
There are three common manufacturing methods for flat bars: hot rolling, cold rolling, and cold drawing.
Hot rolling: This process involves heating steel billets to a high temperature and then rolling them into flat bars. It requires high temperatures during processing and offers fast forming speed.
Cold rolling: This method forms flat bars by rolling hot-rolled steel at room temperature on a cold rolling mill. It helps reduce the thickness of the steel bar and improves surface quality.
Cold drawing: This process involves drawing square or round steel into flat bars at room temperature. It does not generate heat during processing and maintains high dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
Hot-Rolled vs Cold-Rolled vs Cold-Drawn Flat Bar Rails: Visual Differences?
| Process Type | Surface Appearance | Dimensional Accuracy | Cross-Section Shape |
| Hot-Rolled | Rough surface with mill scale; dark gray or reddish tone; visible pitting and bumps | Low; noticeable variations in width and thickness; irregular edges | Irregular; corners are rounded or beveled |
| Cold-Rolled | Smooth and flat surface; uniform silver-gray color with metallic sheen | Higher; more consistent width and thickness; slightly rounded edges | Relatively regular; corners are smooth |
| Cold-Drawn | Bright silver surface with the highest gloss and cleanliness | Highest; minimal size deviation, difficult to detect by eye; sharp edges | Most regular; nearly right-angled corners and excellent straightness |
Looking for flat bar rails for cranes, mining carts?
We provide flat bar rails in various widths, thicknesses, and finishes.
What is the intended use?
Do you need machining, coating, or anti-slip finishing?
Is there a specific profile or weight constraint?
Contact us with your specs—we’ll provide a practical, customized offer.
